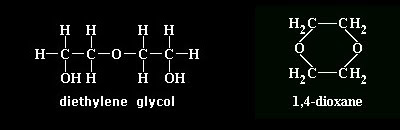Colligative Properties of Dilute Solutions of Non-volatile Solute
Together with the freezing point depression, boiling point elevation and osmotic pressure are properties of dilute solutions that depend on the amount of solute present.
The relationship of boiling point elevation with the amount of solute present is expressed by the equation:

For osmotic pressure, the equation is as follows:


Boiling Point Elevation Problems
| 1. | If a solution of 163.65 g of an unknown compound in 1330 g of benzene has a boiling point of 82.75° C, what is the molecular weight of the solute? The boiling point of benzene is 80.2° C. (Kb = 2.53°C-kg/mol) |
| Answer: 122.08 g/mol |
| |
| 2. | Determine the boiling point of a benzoic acid solution containing 151.86 g of benzoic acid and 1.09 kg of benzene. Assume standard atmospheric pressure. (mol. wt. of benzoic acid = 122.1232 ; Kb = 2.53°C-kg/mol; benzeneTb = 80.2° C) |
| Answer: 83.09° C |
| |
| 3. | An aqueous solution of succinic acid has a concentration of 3.09 molal. Calculate the approximate boiling point of the solution. Water boils at 100°C at standard atmospheric pressure. Kb for water is 0.512°C-kg/mol. |
| Answer: 101.58° C |
| |
| 4. | Determine the boiling point of a beta-naphthol solution containing 282.83 g of beta-naphthol and 1.34 kg of ethanol. Assume standard atmospheric pressure. (mol. wt. of beta-naphthol = 144.1726 ; Kb = 1.22°C-kg/mol; ethanolTb = 78.5° C) |
| Answer: 80.29° C |
| |

| 5. | Find the boiling point of a solution of 63.76 g alpha-naphthol in 1930 g benzene. The boiling point of benzene is 80.2° C. (mol. wt. of alpha-naphthol = 144.1726 ; Kb = 2.53°C-kg/mol) |
| Answer: 80.78° C |
| |
| 6. | Determine the boiling point of an alpha-naphthol solution containing 97.62 g of alpha-naphthol and 0.29 kg of ethanol. Assume standard atmospheric pressure. (mol. wt. of alpha-naphthol = 144.1726 ; Kb = 1.22°C-kg/mol; ethanolTb = 78.5° C) |
| Answer: 81.35° C |
| |
| 7. | Determine the boiling point of an aniline solution containing 172.76 g of aniline and 5.59 kg of benzene. Assume standard atmospheric pressure. (mol. wt. of aniline = 93.128 ; Kb = 2.53°C-kg/mol; benzeneTb = 80.2° C) |
| Answer: 81.04° C |
| |
| 8. | Find the boiling point of a solution of 63.29 g glucose in 140 g ethanol. The boiling point of ethanol is 78.5° C. (mol. wt. of glucose = 180.1572 ; Kb = 1.22°C-kg/mol) |
| Answer: 81.56° C |
| |


| 9. | If a solution of 151.33 g of an unknown compound in 770 g of ethanol has a boiling point of 79.83° C, what is the molecular weight of the solute? The boiling point of ethanol is 78.5° C. (Kb = 1.22°C-kg/mol) |
| Answer: 180.28 g/mol |
| |
| 10. | Determine the boiling point of a glucose solution containing 396.10 g of glucose and 2.71 kg of ethanol. Assume standard atmospheric pressure. (mol. wt. of glucose = 180.1572 ; Kb = 1.22°C-kg/mol; ethanolTb = 78.5° C) |
| Answer: 79.49° C |
| |
| 11. | If a solution of 223.85 g of an unknown compound in 3040 g of ethanol has a boiling point of 79.33° C, what is the molecular weight of the solute? The boiling point of ethanol is 78.5° C. (Kb = 1.22°C-kg/mol) |
| Answer: 108.23 g/mol |
| |
| 12. | If a solution of 325.83 g of an unknown compound in 1850 g of ethanol has a boiling point of 79.99° C, what is the molecular weight of the solute? The boiling point of ethanol is 78.5° C. (Kb = 1.22°C-kg/mol) |
| Answer: 144.21 g/mol |
| |

| 13. | Determine the boiling point of a succinic acid solution containing 123.46 g of succinic acid and 0.34 kg of water. Assume standard atmospheric pressure. (mol. wt. of succinic acid = 118.089 ; Kb = 0.512°C-kg/mol; waterTb = 100° C) |
| Answer: 101.57° C |
| |
| 14. | An aqueous solution of 1,4-dioxane has a concentration of 2.27 molal. Calculate the approximate boiling point of the solution. Water boils at 100°C at standard atmospheric pressure. Kb for water is 0.512°C-kg/mol. |
| Answer: 101.16° C |
| |
| 15. | If a solution of 205.38 g of an unknown compound in 770 g of water has a boiling point of 100.76° C, what is the molecular weight of the solute? The boiling point of water is 100° C. (Kb = 0.512°C-kg/mol) |
| Answer: 179.69 g/mol |
| |
| 16. | Determine the boiling point of a 1,4-dioxane solution containing 71.62 g of 1,4-dioxane and 0.44 kg of water. Assume standard atmospheric pressure. (mol. wt. of 1,4-dioxane = 88.106 ; Kb = 0.512°C-kg/mol; waterTb = 100° C) |
| Answer: 100.95° C |
| |
| 17. | Find the boiling point of a solution of 253.02 g diphenyl ether in 1600 g ethanol. The boiling point of ethanol is 78.5° C. (mol. wt. of diphenyl ether = 170.2104 ; Kb = 1.22°C-kg/mol) |
| Answer: 79.63° C |
| |

| 18. | If a solution of 116.26 g of an unknown compound in 210 g of water has a boiling point of 102.14° C, what is the molecular weight of the solute? The boiling point of water is 100° C. (Kb = 0.512°C-kg/mol) |
| Answer: 132.45 g/mol |
| |
| 19. | An aqueous solution of glycerol has a concentration of 3.12 molal. Calculate the approximate boiling point of the solution. Water boils at 100°C at standard atmospheric pressure. Kb for water is 0.512°C-kg/mol. |
| Answer: 101.6° C |
| |
| 20. | Find the boiling point of a solution of 255.1 g pyrene in 1600 g benzene. The boiling point of benzene is 80.2° C. (mol. wt. of pyrene = 202.255 ; Kb = 2.53°C-kg/mol) |
| Answer: 82.19° C |
| |
| 21. | Determine the boiling point of a solution containing 178.17 g of benzyl alcohol and 1.14 kg of ethanol. Assume standard atmospheric pressure. (mol. wt. of benzyl alcohol = 108.1396 ; Kb = 1.22°C-kg/mol; ethanolTb = 78.5° C) |
| Answer: 80.26° C |
| |

| 22. | Find the boiling point of a solution of 420.41 g phenanthrene in 2170 g benzene. The boiling point of benzene is 80.2° C. (mol. wt. of phenanthrene = 178.233 ; Kb = 2.53°C-kg/mol) |
| Answer: 82.95° C |
| |
| 23. | If a solution of 431.32 g of an unknown compound in 2490 g of benzene has a boiling point of 82.66° C, what is the molecular weight of the solute? The boiling point of benzene is 80.2° C. (Kb = 2.53°C-kg/mol) |
| Answer: 178.15 g/mol |
| |
| 24. | Find the boiling point of a solution of 91.33 g anthracene in 580 g benzene. The boiling point of benzene is 80.2° C. (mol. wt. of anthracene = 178.233 ; Kb = 2.53°C-kg/mol) |
| Answer: 82.44° C |
| |
| 25. | Determine the boiling point of a phenol solution containing 184.34 g of phenol and 2.42 kg of benzene. Assume standard atmospheric pressure. (mol. wt. of phenol = 94.1128 ; Kb = 2.53°C-kg/mol; benzeneTb = 80.2° C) |
| Answer: 82.25° C |
| |
Osmotic Pressure Problems
| 1. | Calculate the osmotic pressure of a 0.871 L solution containing 16.62 g of diethylene glycol at 4° C. ( mol. wt. of diethylene glycol = 106.1212; R = 0.082057 L-atm/K-mol ) |
| Answer: 4.09 atm |
| |
| 2. | A solution containing 6.48 g of a non-electrolyte in 0.539 kg of water has an osmotic pressure of 2.306 atm at 3° C. What is the molecular weight of the solute? ( R = 0.082057 L-atm/K-mol ) |
| Answer: 118.07 g/mol |
| |
| 3. | A solution containing 27.17 g of an organic solute in 738 g of water has an osmotic pressure of 9.349 atm at 12° C. What is the molecular weight of the solute? ( R = 0.082057 L-atm/K-mol ) |
| Answer: 92.09 g/mol |
| |
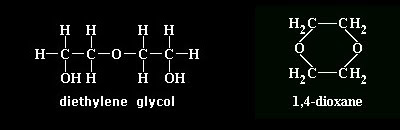
| 4. | 0.851 L of an aqueous solution has 14.31 g 1,4-dioxane. What is the osmotic pressure of this solution at 1° C? ( mol. wt. of 1,4-dioxane = 88.106; R = 0.082057 L-atm/K-mol ) |
| Answer: 4.29 atm |
| |
| 5. | 705 mL of an aqueous solution has 8.98 g glucose. What is the osmotic pressure of this solution at 9° C? ( mol. wt. of glucose = 180.1572; R = 0.082057 L-atm/K-mol ) |
| Answer: 1.64 atm |
| |
| 6. | Calculate the osmotic pressure of a 680 mL solution containing 45.39 g of 1,4-dioxane at 1° C. ( mol. wt. of 1,4-dioxane = 88.106; R = 0.082057 L-atm/K-mol ) |
| Answer: 17.03 atm |
| |


| 7. | Calculate the osmotic pressure of a 865 mL solution containing 6.53 g of sucrose at 5° C. ( mol. wt. of sucrose = 342.2992; R = 0.082057 L-atm/K-mol ) |
| Answer: 0.5 atm |
| |
| 8. | A solution containing 36.14 g of an organic compound in 0.288 kg of water has an osmotic pressure of 22.524 atm at 16° C. What is the molecular weight of the solute? ( R = 0.082057 L-atm/K-mol ) |
| Answer: 132.12 g/mol |
| |


| 9. | Calculate the osmotic pressure of a 953 cm3 solution containing 6.78 g of glycol at 2° C. ( mol. wt. of glycol = 62.0682; R = 0.082057 L-atm/K-mol ) |
| Answer: 2.59 atm |
| |
| 10. | 556 mL of an aqueous solution has 29.96 g glutaric acid. What is the osmotic pressure of this solution at 16° C? ( mol. wt. of glutaric acid = 132.1158; R = 0.082057 L-atm/K-mol ) |
| Answer: 9.67 atm |
| |

 For osmotic pressure, the equation is as follows:
For osmotic pressure, the equation is as follows: